Freeze Drying Alpha 1-4
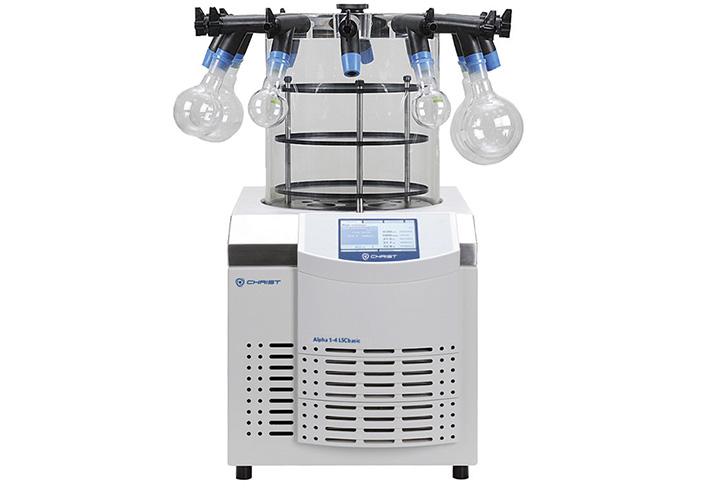

Freeze-drying, also known as lyophilisation, is a meticulous conservation process involving the extraction of water from frozen material, resulting in a solid or liquid product. This method applies to various items such as bacteria and virus cultures, blood plasma, serum fractions, antibodies, sera, vitamins, and proteins, among others, and is typically carried out in ampoules, bottles, glass flasks, plasma bottles, or dishes. It is an effective dehydration technique that minimizes damage by utilizing the physical phenomenon of sublimation, wherein the frozen material is dried under vacuum conditions without undergoing thawing, thereby preserving sensitive components effectively.
In order to prevent melting, boiling, or collapse special care must be taken. Please read the “Basic principles, optimum procedures and applications” for more information.
Technical Data
- Ice condenser capacity: max. 4kg.
- Ice condenser performance: max. 4kg/24h.
- Ice condenser temperature: approx. –54˚C.
- Shelf temperature when freezing and drying inside the ice condenser-chamber: approx. –25˚C to 99˚C.
- Shelf temperature when drying external to the ice condenser chamber: room temperature up to 99˚C.
- Ultimate total vacuum: 0.006mbar
User Info
- The Martin Christ Alpha 1-4 LSCbasic Lyophilizer can be reserved through our Online Reservation System.
- Before using the instrument for the first time, you must receive instruction from Shiran Zafrani.
- Log on to your reservation before starting and log off at the end of use.
- Clean up the inside of the lyophilizer after EACH use.
- If there are problems, please notify BCF staff.